Image Accessibility
Images used throughout the course should be saved as one of the following file types:
- JPG (.jpg)
- SVG (.svg),
- GIF (.gif), or
- PNG (.png).
Images are non-text elements that include photographs, illustrations, diagrams, pictures, charts, graphs, and maps.
Functional vs decorative
Before writing and adding alternative text to your image, its purpose must be determined.
For images that are functional and provide important learning context, you should:
- add a text alternative that serves the equivalent purpose of the image
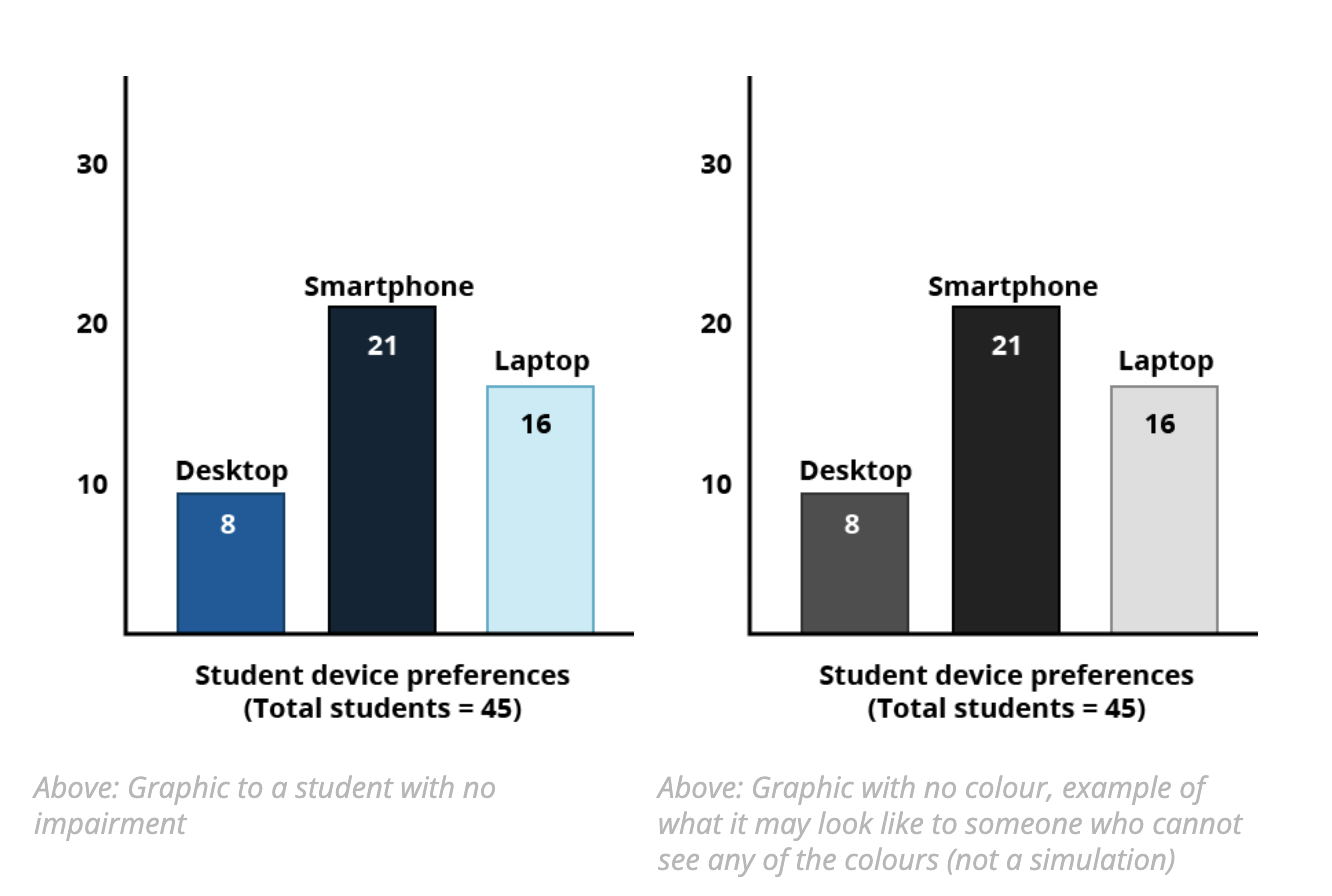
- not use colours as the ONLY visual means of conveying information (eg. referring to colours in a graph with no text).
For images that serve a decorative purpose within the course, you should avoid using any alternative text and simply leave the alt="" tag blank, with empty double quotations.
Adding text alternatives
The 3 ways to provide a text alternative for image content are to:
- describe the image within the page surrounding text
- describe the image using an alt tag, and
- create a description of the image where the image is too complex or conveys detailed information e.g. a graph or chart.
Surrounding page text
The surrounding page text - the text prior to and just after the image placement on screen - can be used when describing more complex images. The surrounding text is visible to all learners, not just those using a text reader and accessing the alt tag, meaning that text explanations are beneficial to all learners.
Alternate text is still required in the alt-text tag when the image has been described and contextualised in the page content.
Alt tags
An alt tag refers to the alt attribute within the <img> HTML code in the course content. Alt tags should be no longer than 100 characters (including spaces and punctuation). This is due to the way most screen readers start by reading out the word “Graphic” followed by the alt tag. If the alt tag is longer than 100 characters, it will stop and read out Graphic again before continuing the remainder of the alt tag. This can be confusing and disorientating for the learner who relies on a screen reader.
In MyUni, alt tags can be added into the Alt text textfield within the Insert/edit image pane from the Rich Content Editor, OR directly into the HTML code.
<img src="images/image.jpg" alt="This is my image description"/>For images that have been determined to be decorative only, check the ‘Decorative image’ checkbox in the Insert/edit image pane or leave the double quotation marks empty inside the HTML alt tag.
<img src="images/image.jpg" alt=" "/>Inline SVG images
Note: Canvas does not currently natively support <svg> tags inserted into the Rich Content Editor.
Since an SVG does not contain any visible text that describes the graphic, the alternative text inside the <svg> tag needs to be included by adding alternate text within the title tags.
<title>A short title of the SVG</title>The alt tag must be added within the first child of its parent element. The SVG alt tag will be used as a tooltip as the pointing device moves over it.
Description text
The final option for providing alternative text is to add a description immediately under the image. To do this correctly, the image and description should be added inside a Figure div. This will give the image a few added properties.
<figure id="image_fig1">
<img src="images/image.jpg" alt="short image description"/> <figcaption>Figure 1.1 This is the image that gives us some context</figcaption>
</figure>To add an image description:
- Add the image inside of a
<figure>HTML as above and create a unique figure ID. - add an alt tag - the image still requires an alt tag even though you are providing a long description
- add a figure caption inside the
<figcaption>tags, and - add the image description within the figure caption tags.
Using colour for graphics
When creating graphics, avoid using only colour to convey information. For example:
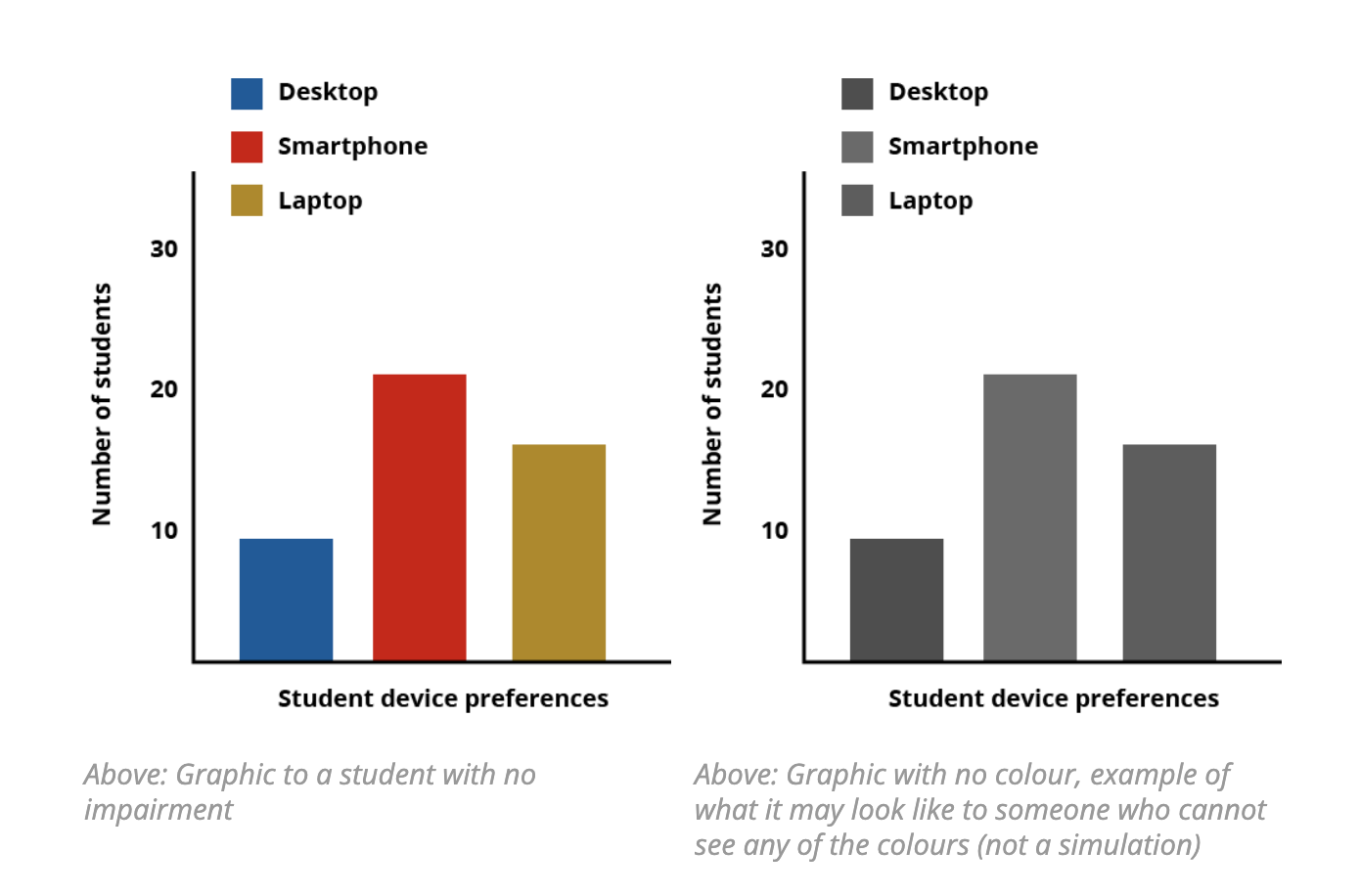
Accessibility guidelines recommend using elements other than colour alone to create associations. An example of this would be using a contrast checker to select appropriate colours, adjusting the axis labels to be more informative and moving value labels (desktop, smartphone and laptop) to sit alongside the data in the chart. For example: